RESOURCE EFFICIENCY AND ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
Environmental efficiency
Moscow Exchange Group hosts annual events to reduce negative impacts on the environment. In its operations, the Group is guided by the laws and regulations of the Russian Federation as well as corporate standards that ensure compliance with environmental requirements.
Key documents:
- Russian environmental legislation and standards
- Waste Generation Standards and Waste Disposal Limits approved by the Moscow Department of Resource Management and Environmental Protection up to February 2023
- Moscow Exchange Environmental Monitoring and Industrial Control Programme
- Administrative Department of Moscow Exchange
Energy efficiency
The Group’s companies have an extensive network of server and computer equipment across two data centres. Improvements in energy efficiency are therefore largely dependent on timely upgrades to the Group’s equipment and the use of IT technologies to transmit information.
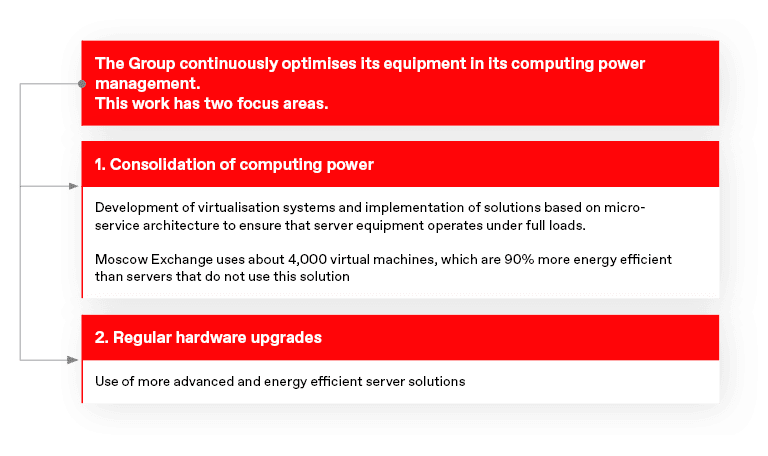
Modern equipment consumes less energy: every new generation of servers is about
To reduce electricity consumption in our offices outside of business hours, hallway lighting systems, ventilation systems, and office air-conditioning systems are automatically turned off. In winter, cold air from outside is used to cool server rooms.
Climate change impact
Direct greenhouse gas emissions are emitted by the Group’s corporate vehicles and the back-up diesel generators used to create electricity in the event of emergency outages on the part of the supplier. Indirect emissions stem from the use of electricity and heat purchased from energy suppliers.
The Group’s modern fleet of vehicles is key to reducing its direct greenhouse gas emissions: most corporate vehicles were manufactured after 2014, and all of them have engines with environmental classifications of IV and V. Measures aimed at reducing indirect emissions are described in Energy Consumption subsection on p. 55.
Water consumption and waste water disposal
303-4 303-5
Moscow Exchange Group strives to improve the efficiency of water consumption at its offices. The Group receives water only from municipal water systems.
Wastewater (including from storm drains) is discharged only to municipal sewage systems, where it is treated in accordance with applicable regulations. No wastewater is discharged into bodies of water or into natural habitats designated as nationally or internationally protected areas. The Group does not operate in regions affected by water scarcity.
Air emissions
305-7
As a result of an inventory of emissions of harmful (polluting) substances into the atmosphere and their sources, it has been established that the sources of impact on atmospheric air are: emergency diesel generator sets (DGS), the operational printing station, and motor transport, including three organised sources of emissions:
- exhaust and ventilation stack of diesel generator set;
- tanks for diesel fuel;
- equipment of the Operational Printing Unit (paper cutting, creasing, paper boring, and thermal bagging of paper products).
and one fugitive, which is exhaust emissions from vehicles entering and exiting the underground car park.
Taking into account that there are substances of hazard classes I and II in the atmospheric emissions, it is planned to implement methods to calculate the volume of emissions, including cases in which technological equipment operates in a modified mode for more than three months, to determine the volume of pollutants in emissions from stationary sources.
Waste management
306-1 306-2 306-5
The activities of Moscow Exchange Group generate office waste (paper, non-industrial waste, fluorescent lamps, etc.), as well as e-waste and waste associated with the vehicle fleet. The Group aims to reduce its office waste and to increase the share of recyclable waste. For this purpose, the Group has taken the following measures:
- introduction of electronic document management to reduce the generation of paper waste;
- collection and disposal of used batteries;
- use of bins for the separate collection and disposal of non-industrial waste.
Moscow Exchange Group does not handle waste on its own, but transfers it for treatment, utilisation, storage, neutralisation, and disposal to specialised organisations holding appropriate licences for handling waste of hazard classes
Waste removal from Moscow Exchange Group facilities is carried out under contracts concluded with specialised organisations in accordance with the requirements of environmental legislation, with subsequent request for documents confirming the actual recycling of waste or its disposal in a solid waste landfill.
Disposal of waste of hazard classes
After the planned replacement of office computer hardware, Moscow Exchange promotes its continued use by offering it to employees or by donating it to schools and orphanages.
The waste generated by Moscow Exchange Group does not directly affect any nationally or internationally protected areas.
